Transplantation Science Symposium (TSS) Asian Regional Meeting 2022
Cutting-Edge Transplant Research -Bench to Bedside-
November 25-26, 2022 - Kyoto, Japan


Transplantation Updates

Transplantation - Highlighted Articles
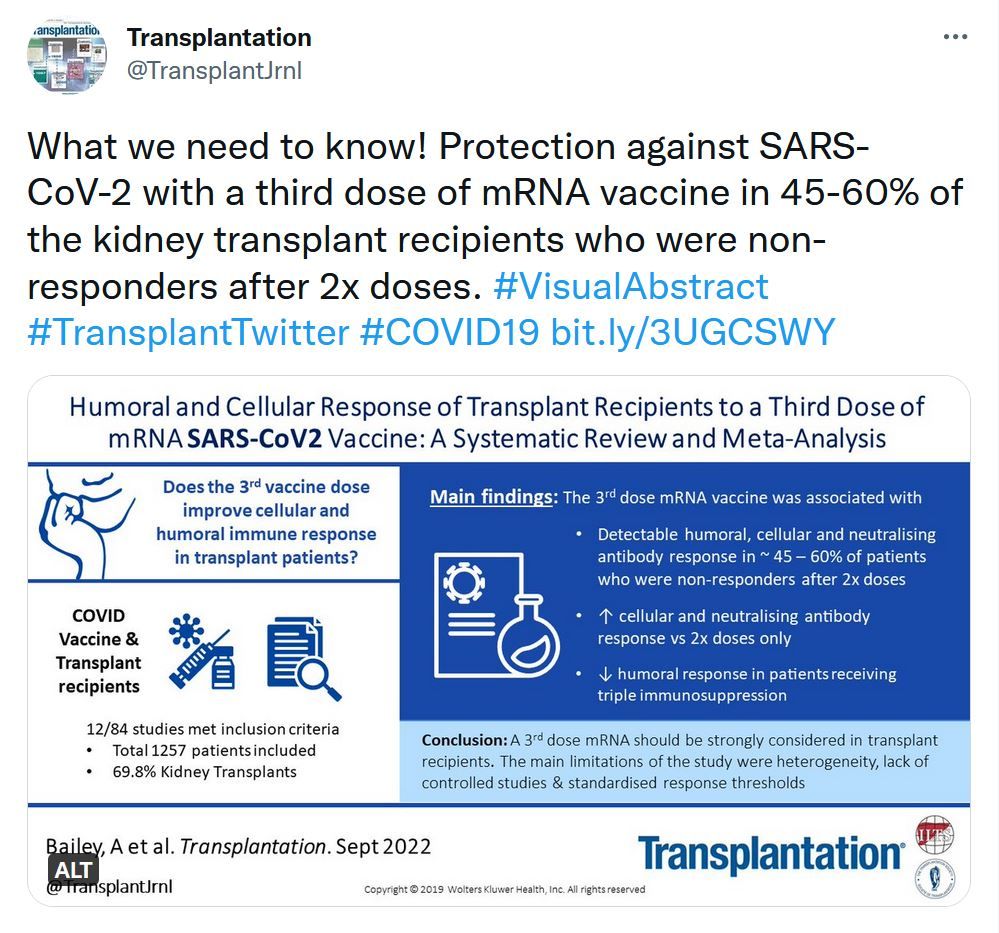
Humoral and Cellular Response of Transplant Recipients to a Third Dose of mRNA SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
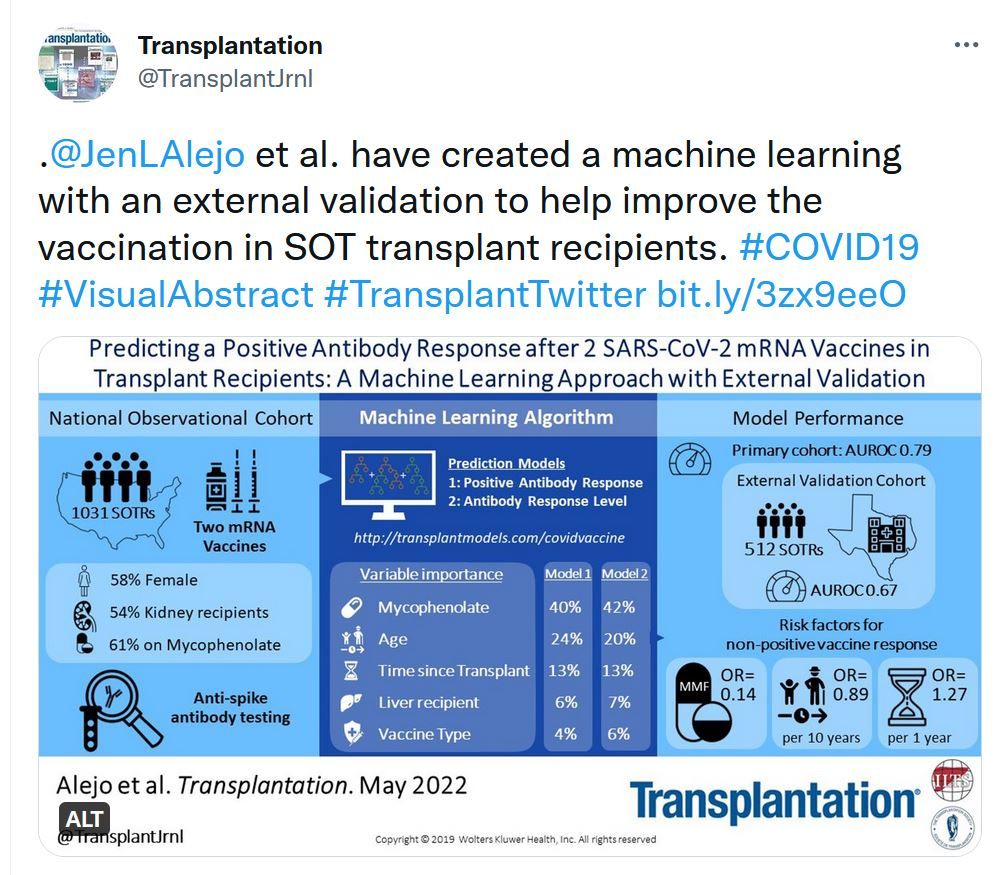
High rates of nonresponse to 2 doses of mRNA severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) vaccine have been reported in transplant recipients. Several studies have investigated the efficacy of a third dose in this population. However, efficacy remains unclear, as response rates vary across studies. Therefore, we conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to determine the efficacy of a third dose of any mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in transplant recipients.Predicting a Positive Antibody Response After 2 SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccines in Transplant Recipients: A Machine Learning Approach With External Validation
olid organ transplant recipients (SOTRs) are less likely to mount an antibody response to SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines. Understanding risk factors for impaired vaccine response can guide strategies for antibody testing and additional vaccine dose recommendations.Transplantation - Week's Most Downloaded Paper
Recommended Treatment for Antibody-mediated Rejection After Kidney Transplantation: The 2019 Expert Consensus From the Transplantion Society Working Group
With the development of modern solid-phase assays to detect anti-HLA antibodies and a more precise histological classification, the diagnosis of antibody-mediated rejection (AMR) has become more common and is a major cause of kidney graft loss. Currently, there are no approved therapies and treatment guidelines are based on low-level evidence. The number of prospective randomized trials for the treatment of AMR is small, and the lack of an accepted common standard for care has been an impediment to the development of new therapies. To help alleviate this, The Transplantation Society convened a meeting of international experts to develop a consensus as to what is appropriate treatment for active and chronic active AMR.Transplantation Direct - Highlighted Tweet
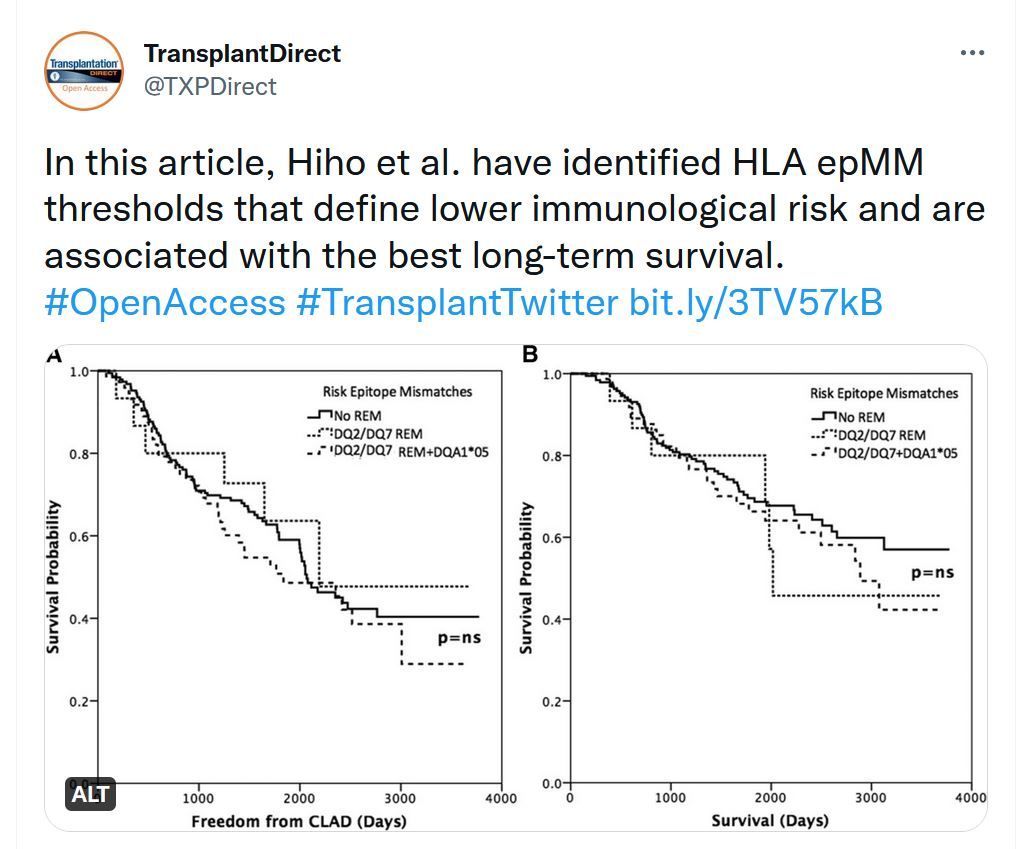
Determining Clinical Thresholds for Donor HLA Eplet Compatibility to Predict Best Outcomes Following Lung Transplantation
Currently, the assessment of immunological risk in lung transplantation (LTx) does not completely consider HLA compatibility at the molecular level. We have previously demonstrated the association of HLA eplets in predicting chronic lung allograft dysfunction following LTx; however, the associations between HLA eplet mismatch (epMM) loads and overall survival are unknown.TTS-ILTS Paired Transplant Centers Program - Apply Today!
Contact
Address
The Transplantation Society
International Headquarters
740 Notre-Dame Ouest
Suite 1245
Montréal, QC, H3C 3X6
Canada
Используйте Вавада казино для игры с бонусом — активируйте промокод и начните выигрывать уже сегодня!